[Note: Today’s selection is a complete sutta from the MN, so it is a bit longer than usual. However the simile is very famous and it’s good to see it in its full context. The simile itself is in bold below if you like to skip to that.]
I have heard that on one occasion the Blessed One was staying near Sāvatthī in Jeta’s Grove, Anāthapiṇḍika’s monastery. Then, as Ven. Māluṅkyaputta was alone in seclusion, this line of thinking arose in his awareness: “These positions that are undisclosed, set aside, discarded by the Blessed One—‘The cosmos is eternal,’ ‘The cosmos is not eternal,’ ‘The cosmos is finite,’ ‘The cosmos is infinite,’ ‘The soul & the body are the same,’ ‘The soul is one thing and the body another,’ ‘After death a Tathāgata exists,’ ‘After death a Tathāgata does not exist,’ ‘After death a Tathāgata both exists & does not exist,’ ‘After death a Tathāgata neither exists nor does not exist’—I don’t approve, I don’t accept that the Blessed One has not disclosed them to me. I’ll go ask the Blessed One about this matter. If he discloses to me that ‘The cosmos is eternal,’ that ‘The cosmos is not eternal,’ that ‘The cosmos is finite,’ that ‘The cosmos is infinite,’ that ‘The soul & the body are the same,’ that ‘The soul is one thing and the body another,’ that ‘After death a Tathāgata exists,’ that ‘After death a Tathāgata does not exist,’ that ‘After death a Tathāgata both exists & does not exist,’ or that ‘After death a Tathāgata neither exists nor does not exist,’ then I will live the holy life under him. If he does not disclose to me that ‘The cosmos is eternal,’ … or that ‘After death a Tathāgata neither exists nor does not exist,’ then I will renounce the training and return to the lower life.”
Then, emerging from his seclusion in the evening, Ven. Māluṅkyaputta went to the Blessed One and, on arrival, having bowed down to him, sat to one side. As he was sitting there he said to the Blessed One, “Lord, just now, as I was alone in seclusion, this line of thinking arose in my awareness: ‘These positions that are undisclosed, set aside, discarded by the Blessed One… I don’t approve, I don’t accept that the Blessed One has not disclosed them to me. I’ll go ask the Blessed One about this matter. If he discloses to me that “The cosmos is eternal,” … or that “After death a Tathāgata neither exists nor does not exist,” then I will live the holy life under him. If he does not disclose to me that “The cosmos is eternal,” … or that “After death a Tathāgata neither exists nor does not exist,” then I will renounce the training and return to the lower life.’
“Lord, if the Blessed One knows that ‘The cosmos is eternal,’ then may he disclose to me that ‘The cosmos is eternal.’ If he knows that ‘The cosmos is not eternal,’ then may he disclose to me that ‘The cosmos is not eternal.’ But if he doesn’t know or see whether the cosmos is eternal or not eternal, then, in one who is unknowing & unseeing, the straightforward thing is to admit, ‘I don’t know. I don’t see.’ … If he doesn’t know or see whether after death a Tathāgata exists… does not exist… both exists & does not exist… neither exists nor does not exist,’ then, in one who is unknowing & unseeing, the straightforward thing is to admit, ‘I don’t know. I don’t see.’”
“Māluṅkyaputta, did I ever say to you, ‘Come, Māluṅkyaputta, live the holy life under me, and I will disclose to you that ‘The cosmos is eternal,’ or ‘The cosmos is not eternal,’ or ‘The cosmos is finite,’ or ‘The cosmos is infinite,’ or ‘The soul & the body are the same,’ or ‘The soul is one thing and the body another,’ or ‘After death a Tathāgata exists,’ or ‘After death a Tathāgata does not exist,’ or ‘After death a Tathāgata both exists & does not exist,’ or ‘After death a Tathāgata neither exists nor does not exist’?”
“No, lord.”
“And did you ever say to me, ‘Lord, I will live the holy life under the Blessed One and (in return) he will disclose to me that ‘The cosmos is eternal,’ or ‘The cosmos is not eternal,’ or ‘The cosmos is finite,’ or ‘The cosmos is infinite,’ or ‘The soul & the body are the same,’ or ‘The soul is one thing and the body another,’ or ‘After death a Tathāgata exists,’ or ‘After death a Tathāgata does not exist,’ or ‘After death a Tathāgata both exists & does not exist,’ or ‘After death a Tathāgata neither exists nor does not exist’?”
“No, lord.”
“Then that being the case, foolish man, who are you to be claiming grievances/making demands of anyone?
“Māluṅkyaputta, if anyone were to say, ‘I won’t live the holy life under the Blessed One as long as he does not disclose to me that “The cosmos is eternal,” … or that “After death a Tathāgata neither exists nor does not exist,”’ the man would die and those things would still remain undisclosed by the Tathāgata.
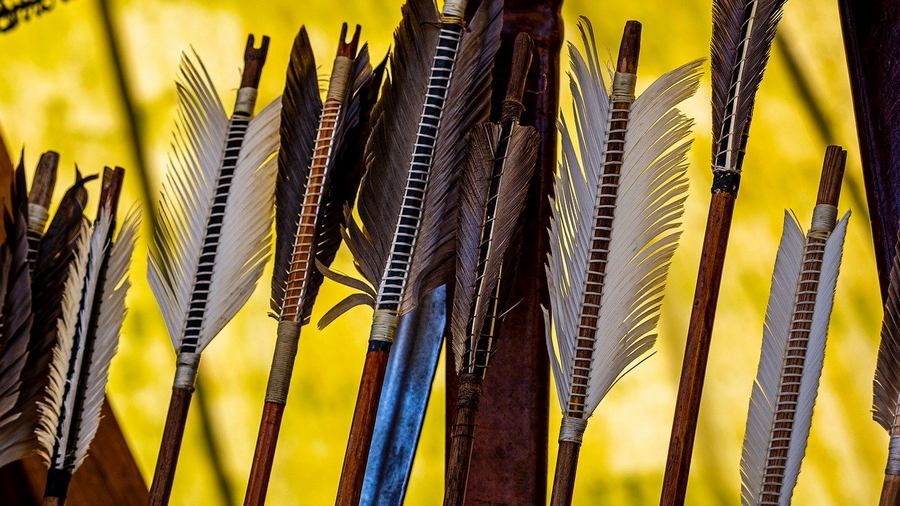
“It’s just as if a man were wounded with an arrow thickly smeared with poison. His friends & companions, kinsmen & relatives would provide him with a surgeon, and the man would say, ‘I won’t have this arrow removed until I know whether the man who wounded me was a noble warrior, a brahman, a merchant, or a worker.’ He would say, ‘I won’t have this arrow removed until I know the given name & clan name of the man who wounded me… until I know whether he was tall, medium, or short… until I know whether he was dark, ruddy-brown, or golden-colored… until I know his home village, town, or city… until I know whether the bow with which I was wounded was a long bow or a crossbow… until I know whether the bowstring with which I was wounded was fiber, bamboo threads, sinew, hemp, or bark… until I know whether the shaft with which I was wounded was wild or cultivated… until I know whether the feathers of the shaft with which I was wounded were those of a vulture, a stork, a hawk, a peacock, or another bird… until I know whether the shaft with which I was wounded was bound with the sinew of an ox, a water buffalo, a langur, or a monkey.’ He would say, ‘I won’t have this arrow removed until I know whether the shaft with which I was wounded was that of a common arrow, a curved arrow, a barbed, a calf-toothed, or an oleander arrow.’ The man would die and those things would still remain unknown to him.
“In the same way, if anyone were to say, ‘I won’t live the holy life under the Blessed One as long as he does not disclose to me that “The cosmos is eternal,” … or that “After death a Tathāgata neither exists nor does not exist,”’ the man would die and those things would still remain undisclosed by the Tathāgata.
“Māluṅkyaputta, it’s not the case that when there is the view, ‘The cosmos is eternal,’ there is the living of the holy life. And it’s not the case that when there is the view, ‘The cosmos is not eternal,’ there is the living of the holy life. When there is the view, ‘The cosmos is eternal,’ and when there is the view, ‘The cosmos is not eternal,’ there is still the birth, there is the aging, there is the death, there is the sorrow, lamentation, pain, despair, & distress whose destruction I make known right in the here & now.
“It’s not the case that when there is the view, ‘The cosmos is finite,’ there is the living of the holy life. And it’s not the case that when there is the view, ‘The cosmos is infinite,’ there is the living of the holy life. When there is the view, ‘The cosmos is finite,’ and when there is the view, ‘The cosmos is infinite,’ there is still the birth, there is the aging, there is the death, there is the sorrow, lamentation, pain, despair, & distress whose destruction I make known right in the here & now.
“It’s not the case that when there is the view, ‘The soul & the body are the same,’ there is the living of the holy life. And it’s not the case that when there is the view, ‘The soul is one thing and the body another,’ there is the living of the holy life. When there is the view, ‘The soul & the body are the same,’ and when there is the view, ‘The soul is one thing and the body another,’ there is still the birth, there is the aging, there is the death, there is the sorrow, lamentation, pain, despair, & distress whose destruction I make known right in the here & now.
“It’s not the case that when there is the view, ‘After death a Tathāgata exists,’ there is the living of the holy life. And it’s not the case that when there is the view, ‘After death a Tathāgata does not exist,’ there is the living of the holy life. And it’s not the case that when there is the view, ‘After death a Tathāgata both exists & does not exist,’ there is the living of the holy life. And it’s not the case that when there is the view, ‘After death a Tathāgata neither exists nor does not exist’ there is the living of the holy life. When there is the view, ‘After death a Tathāgata exists’ … ‘After death a Tathāgata does not exist’ … ‘After death a Tathāgata both exists & does not exist’ … ‘After death a Tathāgata neither exists nor does not exist,’ there is still the birth, there is the aging, there is the death, there is the sorrow, lamentation, pain, despair, & distress whose destruction I make known right in the here & now.
“So, Māluṅkyaputta, remember what is undisclosed by me as undisclosed, and what is disclosed by me as disclosed. And what is undisclosed by me? ‘The cosmos is eternal,’ is undisclosed by me. ‘The cosmos is not eternal,’ is undisclosed by me. ‘The cosmos is finite’ … ‘The cosmos is infinite’ … ‘The soul & the body are the same’ … ‘The soul is one thing and the body another’ … ‘After death a Tathāgata exists’ … ‘After death a Tathāgata does not exist’ … ‘After death a Tathāgata both exists & does not exist’ … ‘After death a Tathāgata neither exists nor does not exist,’ is undisclosed by me.
“And why are they undisclosed by me? Because they are not connected with the goal, are not fundamental to the holy life. They do not lead to disenchantment, dispassion, cessation, calming, direct knowledge, self-awakening, unbinding. That’s why they are undisclosed by me.
“And what is disclosed by me? ‘This is stress,’ is disclosed by me. ‘This is the origination of stress,’ is disclosed by me. ‘This is the cessation of stress,’ is disclosed by me. ‘This is the path of practice leading to the cessation of stress,’ is disclosed by me. And why are they disclosed by me? Because they are connected with the goal, are fundamental to the holy life. They lead to disenchantment, dispassion, cessation, calming, direct knowledge, self-awakening, unbinding. That’s why they are disclosed by me.
“So, Māluṅkyaputta, remember what is undisclosed by me as undisclosed, and what is disclosed by me as disclosed.”
That is what the Blessed One said. Gratified, Ven. Māluṅkyaputta delighted in the Blessed One’s words.
Read this translation of Majjhima Nikāya 63 Cūḷa Māluṅkyovāda Sutta. The Shorter Exhortation to Māluṅkya by Bhikkhu Ṭhanissaro on DhammaTalks.org. Or read a different translation on SuttaCentral.net. Or listen on PaliAudio.com or SC-Voice.net. Or explore the Pali on DigitalPaliReader.online.
Or read a translation in Lietuvių Kalba, ру́сский язы́к, Bengali, Català, Deutsch, Español, Français, हिन्दी, Magyar, Indonesian, Italiano, 日本語, 한국어/조선말, မြန်မာဘာသာ, Norsk, Português, සිංහල, Slovenščina, Srpski, Svenska, ไทย, Tiếng Việt, or 汉语. Learn how to find your language.


 Copyright: Creative Commons Zero (CC0) To the extent possible under law, Bhikkhu Sujato has waived all copyright and related or neighboring rights to his own translations on
Copyright: Creative Commons Zero (CC0) To the extent possible under law, Bhikkhu Sujato has waived all copyright and related or neighboring rights to his own translations on 
 Translations by Bhikkhu Ṭhanissaro are released under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 Unported License. The author considers any sale, including by non-profit entities for non-profit purposes, to be ‘Commercial’ and a copyright violation. To view a copy of this license, visit the
Translations by Bhikkhu Ṭhanissaro are released under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 Unported License. The author considers any sale, including by non-profit entities for non-profit purposes, to be ‘Commercial’ and a copyright violation. To view a copy of this license, visit the 
 All translations on this site by Bhikkhu Bodhi are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License.
Bhikkhu Bodhi, The Middle Length Discourses of the Buddha (Wisdom Publications, 2009), The Connected Discourses of the Buddha (Wisdom Publications, 2000), The Numerical Discourses of the Buddha (Wisdom Publications, 2012).
All translations on this site by Bhikkhu Bodhi are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License.
Bhikkhu Bodhi, The Middle Length Discourses of the Buddha (Wisdom Publications, 2009), The Connected Discourses of the Buddha (Wisdom Publications, 2000), The Numerical Discourses of the Buddha (Wisdom Publications, 2012).


























