[Note: This is part of a larger sutta that begins with a discussion on the Buddha’s rule for the monastics to only eat in the morning time.]
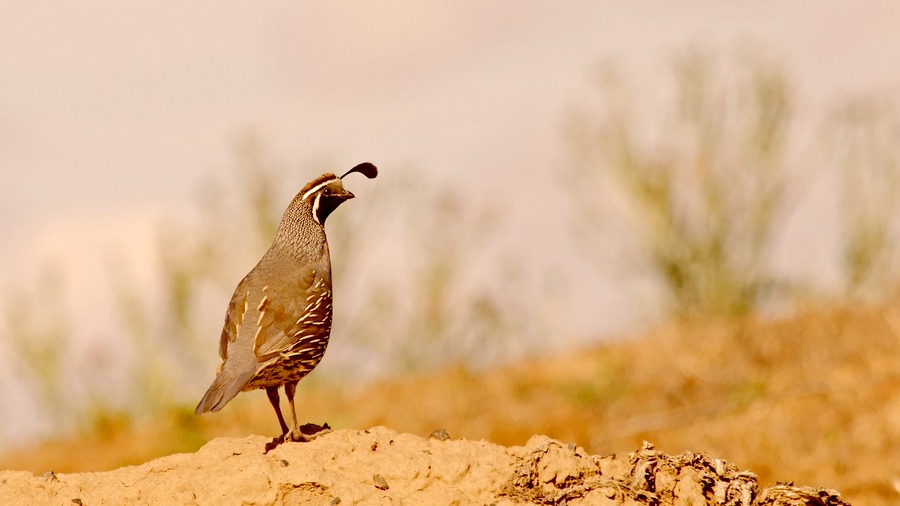
“Suppose a quail were snared by a rotting creeper, by which it could expect injury, captivity, or death, and someone were to say, ‘This rotting creeper by which this quail is snared, and by which she could expect injury, captivity, or death, is for her a weak snare, a feeble snare, a rotting snare, an insubstantial snare.’ Would the person speaking that way be speaking rightly?”
“No, lord. That rotting creeper… is for her a strong snare, a thick snare, a heavy snare, an unrotting snare, and a thick yoke.
“In the same way, Udāyin, there are some worthless men who, when I tell them, ‘Abandon this,’ say: ‘What? This little, trifling thing? He’s too much of a stickler, this contemplative.’ They don’t abandon it. They’re rude to me and to the monks keen on training. For them that’s a strong snare, a thick snare, a heavy snare, an unrotting snare, and a thick yoke.
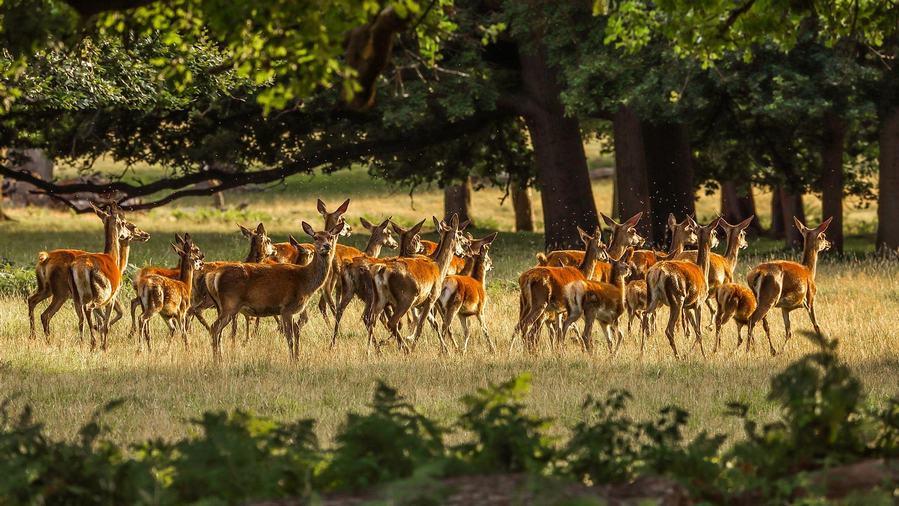
“Now there are some clansmen who, when I tell them, ‘Abandon this,’ say: ‘What? The Blessed One has us abandon, the One Well-Gone has us relinquish this little, trifling thing?’ But they abandon it and are not rude to me or to the monks keen on training. Having abandoned it, they live unconcerned, unruffled, their wants satisfied, with their mind like a wild deer. For them that’s a weak snare, a feeble snare, a rotting snare, an insubstantial snare.
“Suppose a royal elephant—immense, pedigreed, accustomed to battles, its tusks like chariot poles—were snared with thick leather snares, but by twisting its body a bit it could break & burst those snares and go off wherever it liked. And suppose someone were to say, ‘Those thick leather snares by which the royal elephant… was snared, but which—by twisting its body a bit— it could break & burst and go off wherever it liked: for him they were a strong snare, a thick snare, a heavy snare, an unrotting snare, and a thick yoke.’ Would the person speaking that way be speaking rightly?’
“No, lord. Those thick leather snares… were for him a weak snare, a feeble snare, a rotting snare, an insubstantial snare.”
“In the same way, Udāyin, there are some clansmen who, when I tell them, ‘Abandon this,’ say: ‘What? The Blessed One has us abandon, the One Well-Gone has us relinquish this little, trifling thing?’ But they abandon it and are not rude to me or to the monks keen on training. Having abandoned it, they live unconcerned, unruffled, their wants satisfied, with their mind like a wild deer. For them that’s a weak snare, a feeble snare, a rotting snare, an insubstantial snare.
“Suppose there were a poor person, penniless & indigent, with a single little shack—dilapidated, open to the crows, not the best sort; and a single bed—dilapidated, not the best sort; and a single pot of rice & gourd seeds—not the best sort; and a single wife, not the best sort. He would go to a park and see a monk—his hands & feet washed, after a delightful meal, sitting in the cool shade, committed to the heightened mind. The thought would occur to him: How happy the contemplative state! How free of disease the contemplative state! O that I—shaving off my hair & beard and donning the ochre robe—might go forth from the household life into homelessness!’ But being unable to abandon his single little shack—dilapidated, open to the crows, not the best sort; to abandon his single bed—dilapidated, not the best sort; to abandon his single pot of rice & gourd seeds—not the best sort; and to abandon his single wife, not the best sort, he wouldn’t be able to shave off his hair & beard, to don the ochre robe, or to go forth from the household life into homelessness. And suppose someone were to say, ‘That single little shack—dilapidated, open to the crows, not the best sort; that single bed—dilapidated, not the best sort; that single pot of rice & gourd seeds—not the best sort; and that single wife, not the best sort by which that man was snared, which he was unable to abandon, and because of which he couldn’t shave off his hair & beard, don the ochre robe, and go forth from the household life into homelessness: for him they were a weak snare, a feeble snare, a rotting snare, an insubstantial snare.’ Would the person speaking that way be speaking rightly?”
“No, lord. That single hut… that single bed… that single pot… that single wife… were for that man a strong snare, a thick snare, a heavy snare, an unrotting snare, and a thick yoke.”
“In the same way, Udāyin, there are some worthless men who, when I tell them, ‘Abandon this,’ say: ‘What? This little, trifling thing? He’s too much of a stickler, this contemplative.’ They don’t abandon it. They’re rude to me and to the monks keen on training. For them that’s a strong snare, a thick snare, a heavy snare, an unrotting snare, and a thick yoke.
“Now suppose, Udāyin, that there were a householder or householder’s son—rich, prosperous, & wealthy—with vast amounts of gold ingots, vast amounts of grain, a vast number of fields, a vast amount of land, a vast number of wives, and a vast number of male & female slaves. He would go to a park and see a monk—his hands & feet washed, after a delightful meal, sitting in the cool shade, committed to the heightened mind. The thought would occur to him: How happy the contemplative state! How free of disease the contemplative state! O that I—shaving off my hair & beard and donning the ochre robe—might go forth from the household life into homelessness!’ And being able to abandon his vast amounts of gold ingots, his vast amounts of grain, his vast number of fields, his vast amount of land, his vast number of wives, and his vast number of male & female slaves, he would be able to shave off his hair & beard, to don the ochre robe, and to go forth from the household life into homelessness. Now suppose someone were to say, ‘Those vast amounts of gold ingots… and a vast number of male & female slaves by which that householder or householder’s son was snared but which he was able to abandon so that he could shave off his hair & beard, don the ochre robe, and go forth from the household life into homelessness: for him they were a strong snare, a thick snare, a heavy snare, an unrotting snare, and a thick yoke.’ Would the person speaking that way be speaking rightly?”
“No, lord. Those vast amounts of gold ingots… were for him a weak snare, a feeble snare, a rotting snare, an insubstantial snare.’
“In the same way, Udāyin, there are some clansmen who, when I tell them, ‘Abandon this,’ say: ‘What? The Blessed One has us abandon, the One Well-Gone has us relinquish this little, trifling thing?’ But they abandon it and are not rude to me or to the monks keen on training. Having abandoned it, they live unconcerned, unruffled, their wants satisfied, with their mind like a wild deer. For them that’s a weak snare, a feeble snare, a rotting snare, an insubstantial snare.
Read the entire translation of Majjhima Nikāya 66 Laḍukikopama Sutta. The Quail Simile by Bhikkhu Ṭhanissaro on DhammaTalks.org.
Or read a different translation on SuttaCentral.net or DhammaTalks.org. Or listen on PaliAudio.com or SC-Voice.net. Or explore the Pali on DigitalPaliReader.online.
Or read a translation in Bengali, Català, Deutsch, Español, Français, हिन्दी, Indonesian, Italiano, မြန်မာဘာသာ, Norsk, Português, Română, ру́сский язы́к, සිංහල, Slovenščina, Srpski, ไทย, Tiếng Việt, or 汉语. Learn how to find your language.


 Copyright: Creative Commons Zero (CC0) To the extent possible under law, Bhikkhu Sujato has waived all copyright and related or neighboring rights to his own translations on
Copyright: Creative Commons Zero (CC0) To the extent possible under law, Bhikkhu Sujato has waived all copyright and related or neighboring rights to his own translations on 









 All translations on this site by Bhikkhu Bodhi are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License.
Bhikkhu Bodhi, The Middle Length Discourses of the Buddha (Wisdom Publications, 2009), The Connected Discourses of the Buddha (Wisdom Publications, 2000), The Numerical Discourses of the Buddha (Wisdom Publications, 2012).
All translations on this site by Bhikkhu Bodhi are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License.
Bhikkhu Bodhi, The Middle Length Discourses of the Buddha (Wisdom Publications, 2009), The Connected Discourses of the Buddha (Wisdom Publications, 2000), The Numerical Discourses of the Buddha (Wisdom Publications, 2012).








 Translations by Bhikkhu Ṭhanissaro are released under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 Unported License. The author considers any sale, including by non-profit entities for non-profit purposes, to be ‘Commercial’ and a copyright violation. To view a copy of this license, visit the
Translations by Bhikkhu Ṭhanissaro are released under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 Unported License. The author considers any sale, including by non-profit entities for non-profit purposes, to be ‘Commercial’ and a copyright violation. To view a copy of this license, visit the 









